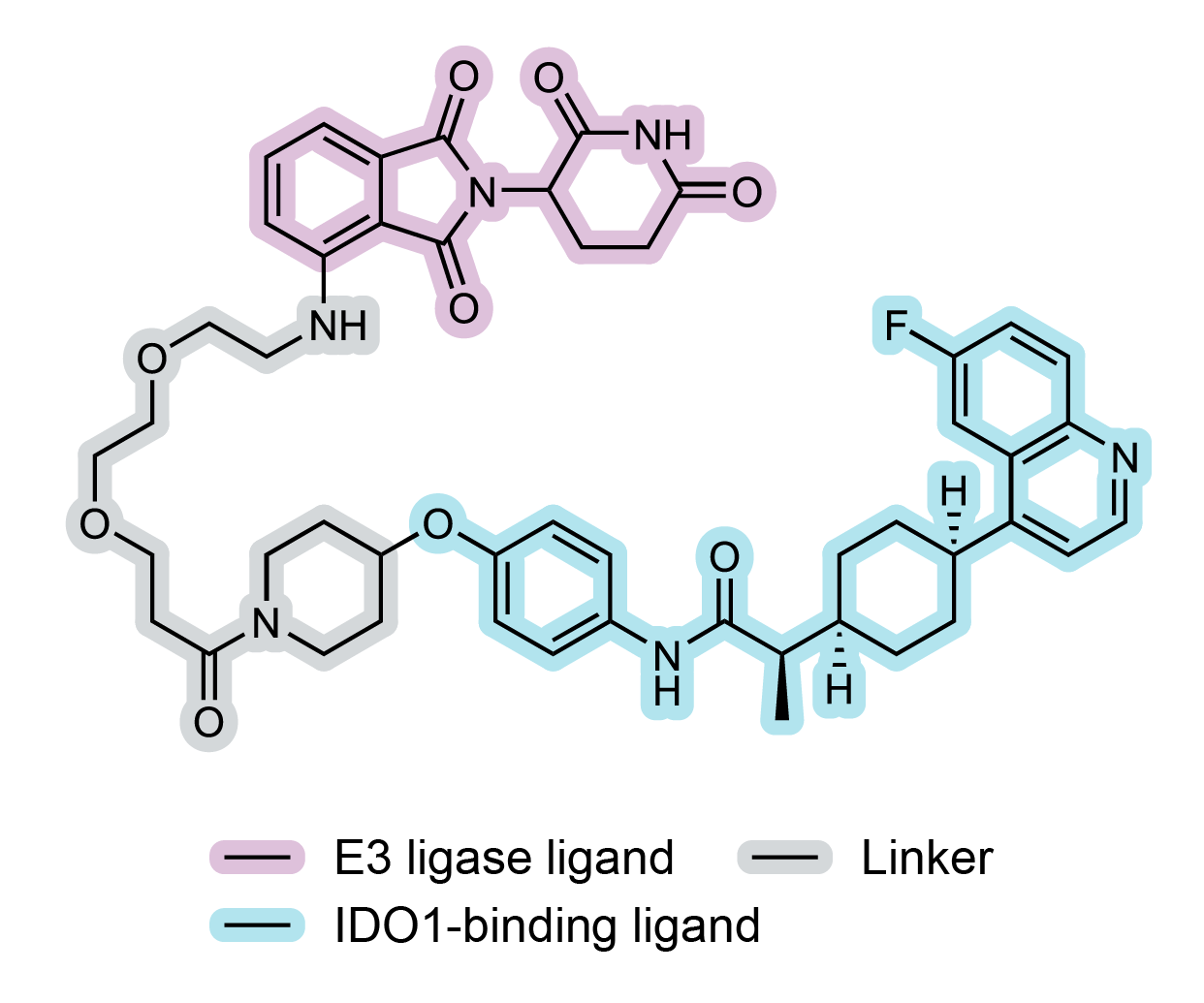
Targeted protein degradation is a promising therapeutic strategy to eliminate, rather than inhibit, unwanted disease-related proteins.
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) are heterobifunctional molecules consisting of two binding domains connected through a linker, of which one domain binds the target protein and the other engages an E3 ubiquitin ligase, ultimately resulting in degradation of the target.
A key feature of PROTACs is their potential for targeting ‘undruggable’ proteins that lack an active site.
In the case of tryptophan-catabolizing enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), a promising drug target for cancer immunotherapy and neurodegenerative diseases, PROTACs may not only be applied to suppress catalytic activity, but also to constrain non-enzymatic signaling that is not targeted by active site inhibitors.
An IDO1-targeting PROTAC (NU223612)1 derived from the IDO1 inhibitor linrodostat was synthesized (Figure 1).
The PROTAC was evaluated in both our cellular protein degradation assay with U-87 MG cells and cellular NFK Green™ assay for IDO1 inhibition with MDA-MB-231 cells.
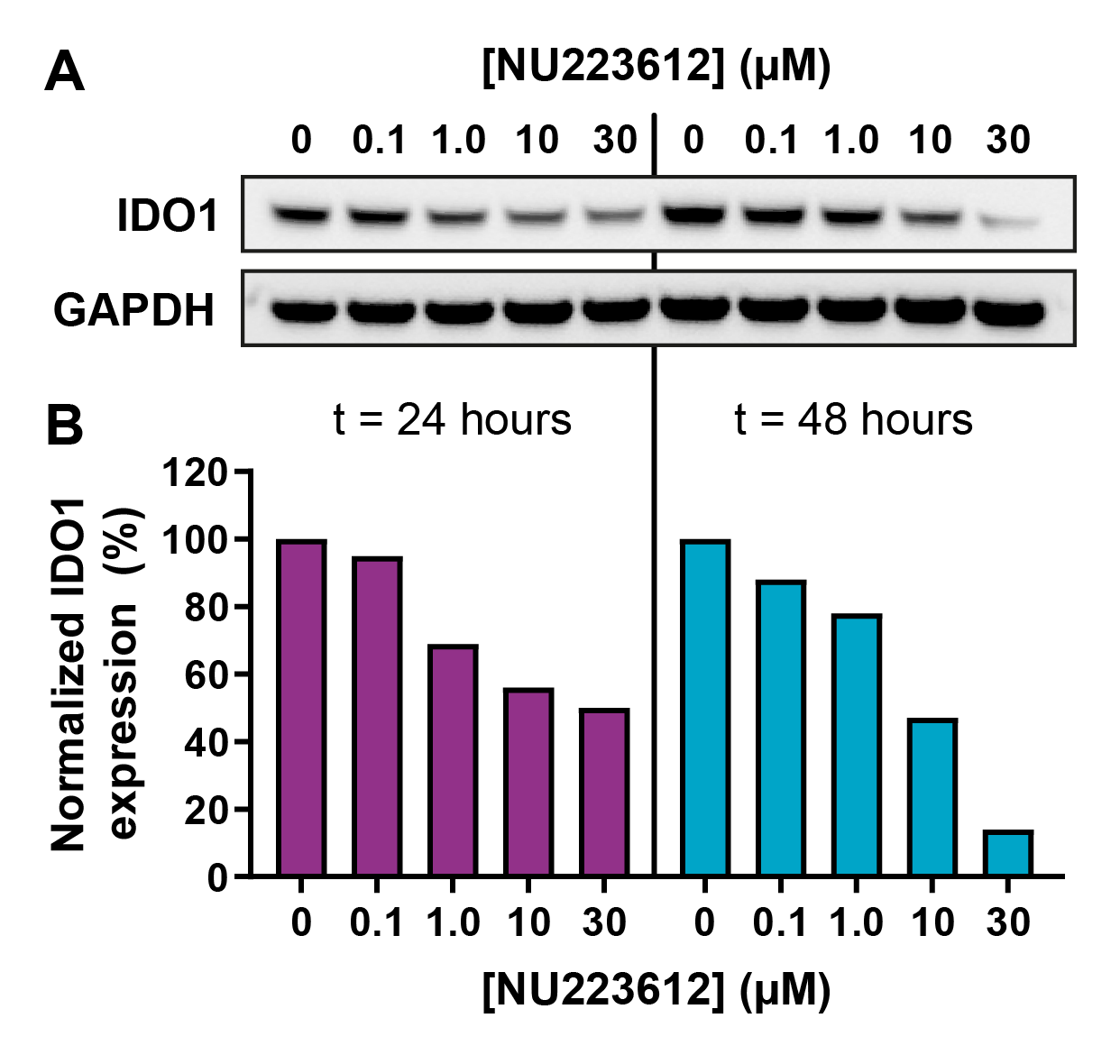
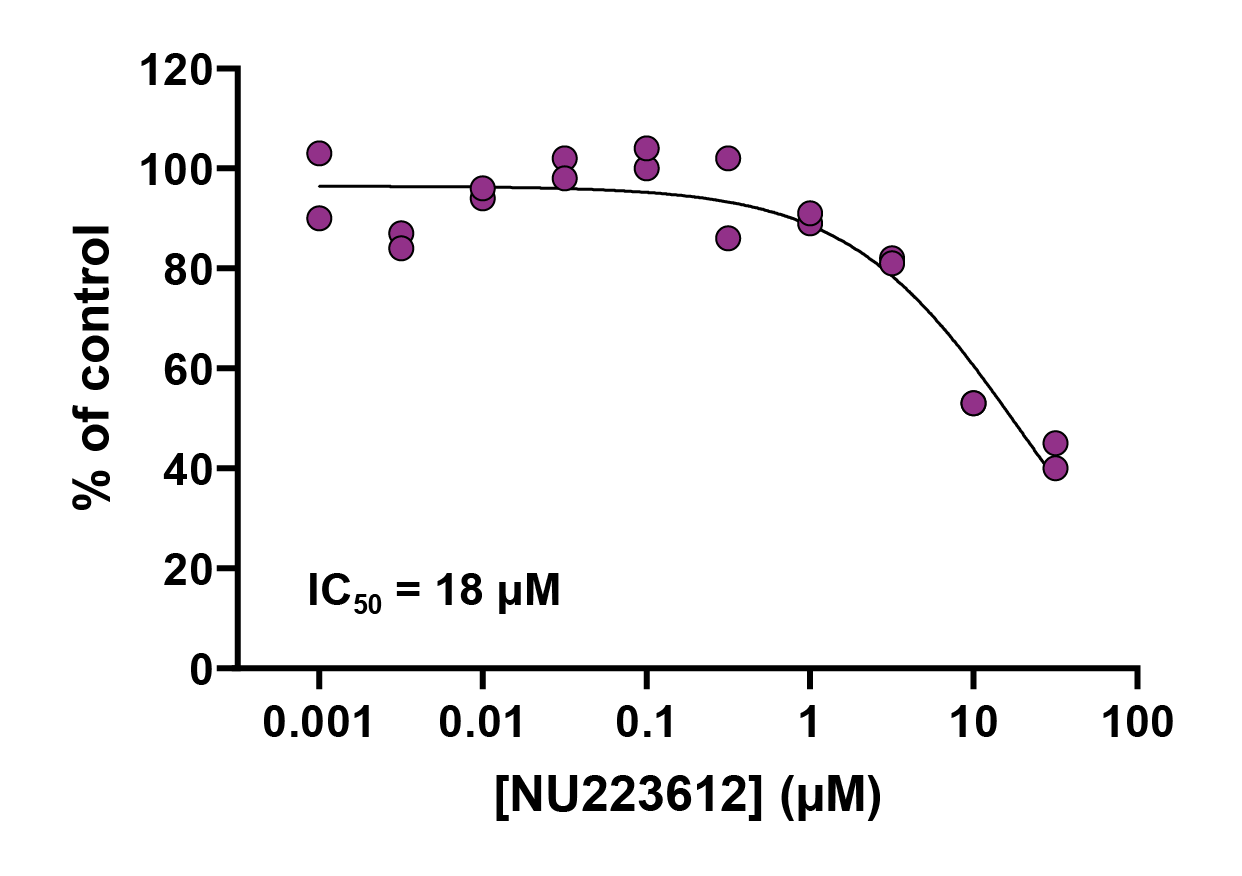
The PROTAC successfully induced degradation of IDO1 at different concentrations and timepoints as shown by Western blot (Figure 2), and inhibited IDO1 enzymatic activity in cells with similar potency (Figure 3).
We can efficiently synthesize PROTACs for other promising targets through our
modular toolbox platform comprising a selection of E3 ligase ligands, a set of > 200 linker constructs and a variety of coupling conditions.
Reference
1. Bollu et al. (2022) Identification and characterization of a novel indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 protein degrader for glioblastoma. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 65, 15642–15662