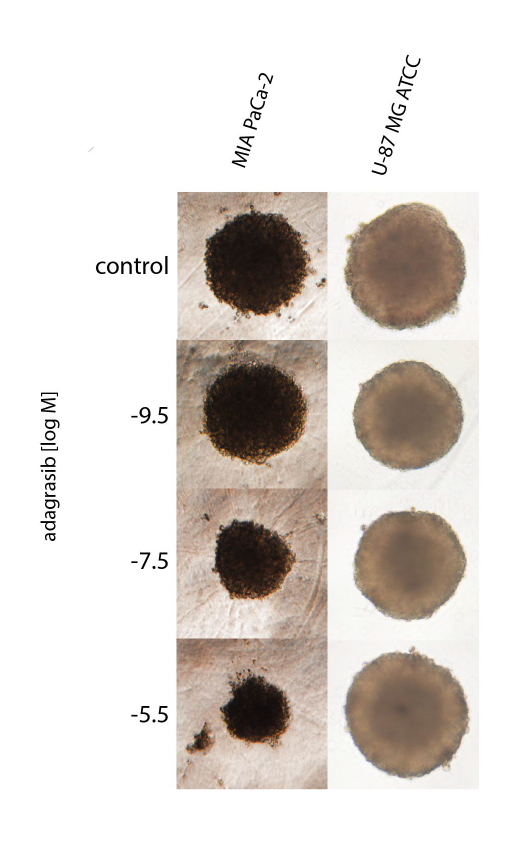
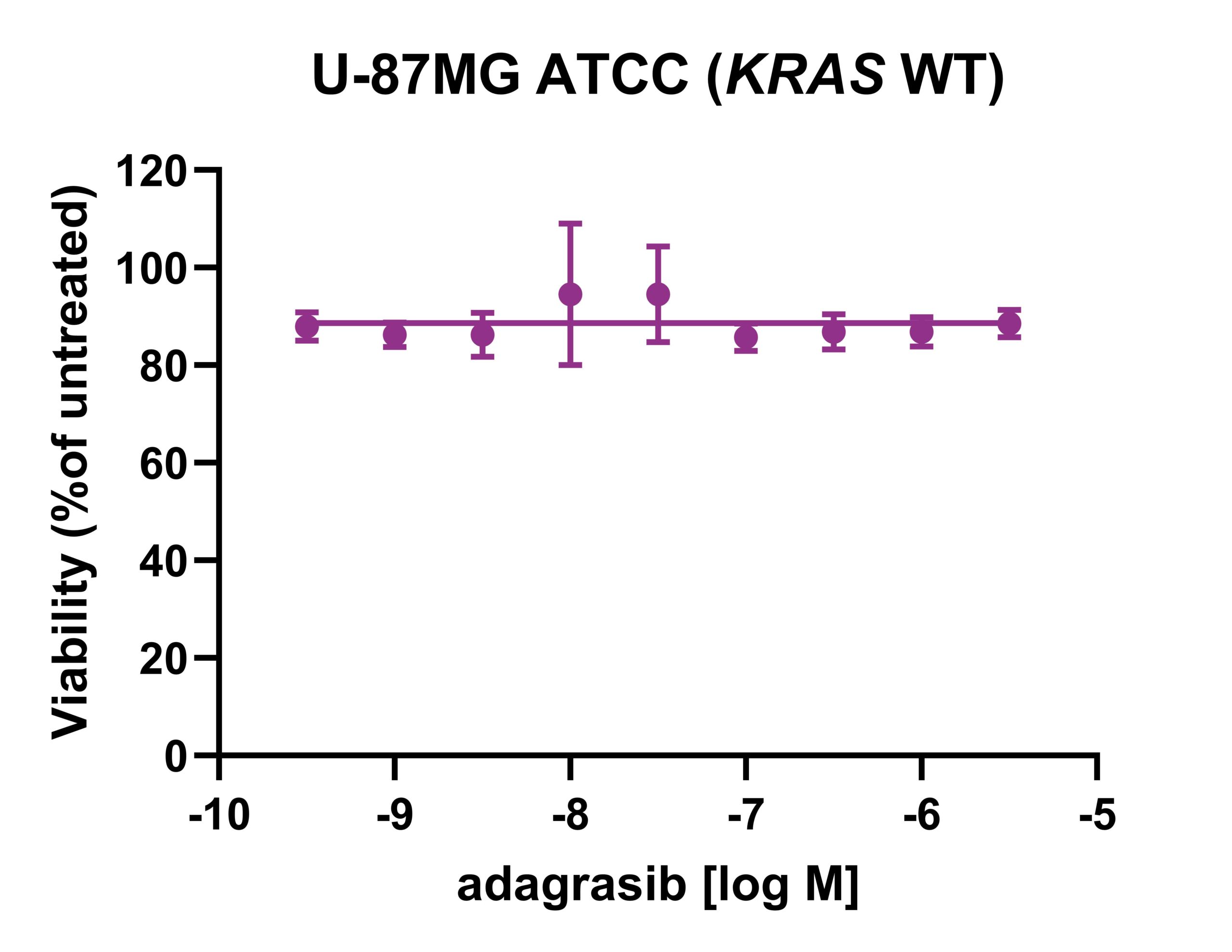
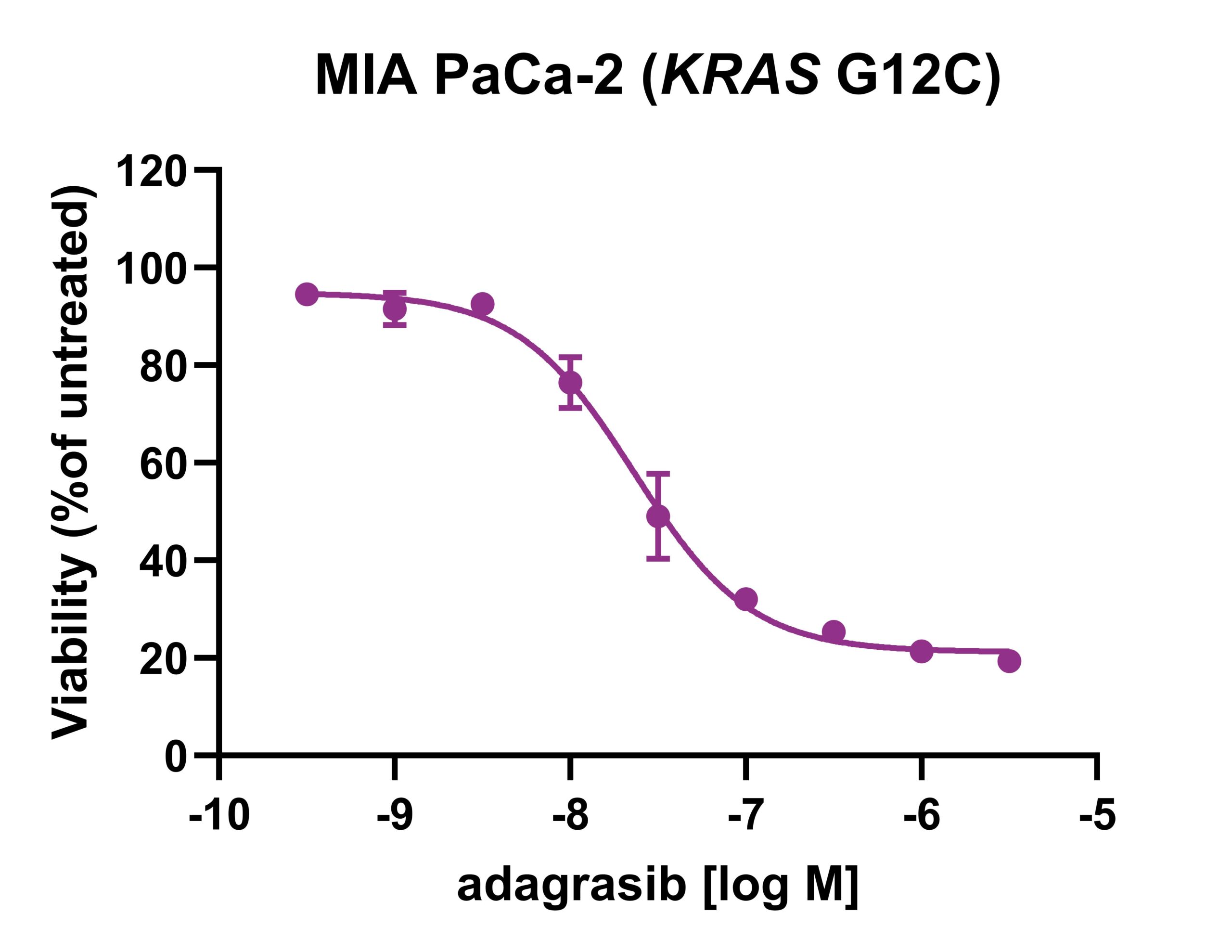
Sensitivity of adagrasib in spheroids of KRAS wild-type and
KRAS G12C mutant cell line
References
1. Djordjevic et al. (2006) Cell-cell interactions in spheroids maintained in suspension. Acta Oncologica 45(4), 412-420.
2. Lama et al. (2013) Development, validation and pilot screening of an in vitro multi-cellular three-dimensional cancer spheroid assay for anti-cancer drug testing. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 21(4), 922-931.
3. Hamer et al. (2008) The genomic profile of human malignant glioma is altered early in primary cell culture and preserved in spheroids. Oncogene 27(14), 2091-2096.